Portal:Somerset
The Somerset Portal
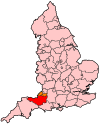
Somerset (/ˈsʌmərsɪt, -sɛt/ SUM-ər-sit, -set; archaically Somersetshire /ˈsʌmərsɪt.ʃɪər, -sɛt-, -ʃər/ SUM-ər-sit-sheer, -set-, -shər) is a ceremonial county in South West England. It is bordered by the Bristol Channel, Gloucestershire, and Bristol to the north, Wiltshire to the east and the north-east, Dorset to the south-east, and Devon to the south-west. The largest settlement is the city of Bath, and the county town is Taunton.
Somerset is a predominantly rural county, especially to the south and west, with an area of 4,171 km2 (1,610 sq mi) and a population of 965,424. After Bath (101,557), the largest settlements are Weston-super-Mare (82,418), Taunton (60,479), Yeovil (49,698) and Frome (28,559). Wells (12,000) is a city, the second-smallest by population in England. For local government purposes the county comprises three unitary authority areas: Bath and North East Somerset, North Somerset, and Somerset. Bath and North East Somerset Council is a member of the West of England Combined Authority.
The centre of Somerset is dominated by the Levels, a coastal plain and wetland. The north-east contains part of the Cotswolds uplands and all of the Mendip Hills, which are both national landscapes; the west contains the Quantock Hills and part of the Blackdown Hills, which are also national landscapes, and most of Exmoor, a national park. The major rivers of the county are the Avon, which flows through Bath and then Bristol, and the Axe, Brue, and Parrett, which drain the Levels.
There is evidence of Paleolithic human occupation in Somerset, and the area was subsequently settled by the Celts, Romans and Anglo-Saxons. The county played a significant part in Alfred the Great's rise to power, and later the English Civil War and the Monmouth Rebellion. In the later medieval period its wealth allowed its monasteries and parish churches to be rebuilt in grand style; Glastonbury Abbey was particularly important, and claimed to house the tomb of King Arthur and Guinevere. The city of Bath is famous for its Georgian architecture, and is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The county is also the location of Glastonbury Festival, one of the UK's major music festivals. (Full article...)
Selected article

Many of the museums are in listed buildings. In the United Kingdom, this signifies a building which has been placed on the Statutory List of Buildings of Special Architectural or Historic Interest. In England and Wales, the authority for listing is granted by the Planning (Listed Buildings and Conservation Areas) Act 1990, and is presently administered by English Heritage. Listed buildings in danger of decay are included on English Heritage's Buildings at Risk Register. There are three types of listed status: Grade I, for buildings "of exceptional interest, sometimes considered to be internationally important"; Grade II*, for "particularly important buildings of more than special interest"; and Grade II, for buildings that are "nationally important and of special interest".
Many of the museums have been accredited by the Museums, Libraries and Archives Council, which sets national standards for museums in the UK. Several are art galleries providing space for the exhibition of art, or are philatelic, regimental, science, aviation, transport, railway, toy, religious or sports museums, but the majority are local museums. There are also several historic house museums owned or managed by the National Trust or English Heritage. (Full article...)
Selected biography -
Hugh of Wells (died 7 February 1235) was a medieval Bishop of Lincoln. He began his career in the diocese of Bath, where he served two successive bishops, before joining royal service under King John of England. He served in the royal administration until 1209, when he was elected to the see, or bishopric, of Lincoln. When John was excommunicated by Pope Innocent III in November 1209, Hugh went into exile in France, where he remained until 1213.
When he returned to England, he continued to serve both John and John's son King Henry III, but spent most of his time in his diocese. He introduced new administrative methods into the diocese, as well as working to improve the educational and financial well-being of his clergy and to secure the canonisation of his predecessor Hugh of Avalon as a saint in 1220. Although the medieval writer Matthew Paris accused Hugh of being opposed to monastic houses and monks, there is little evidence of the bishop being biased, and after his death on 7 February 1235 parts of his estate were left to religious houses, including nunneries. (Full article...)Districts of Somerset

- Somerset (Unitary)
- North Somerset (Unitary)
- Bath and North East Somerset (Unitary)
Subcategories
Related portals
Selected images
Selected settlement
Co-ordinates 51°14′15″N 2°59′37″W / 51.2376°N 2.9935°W
Burnham-on-Sea is a town at the mouth of the River Parrett on Bridgwater Bay. Burnham was a small village until the late 18th century, when it began to grow because of its popularity as a seaside resort. It forms part of the parish of Burnham-on-Sea and Highbridge. According to the 2001 census the population of the parish was 18,401.
The position of the town on the edge of the Somerset Levels, where they meet the Bristol Channel, has resulted in a history dominated by land reclamation and sea defences since Roman times. Burnham was seriously affected by the Bristol Channel floods of 1607, and various flood defences have been installed since then. In 1911, a concrete sea wall was built, and after the Second World War further additions to the defences were made, using the remains of a Mulberry harbour. The present curved concrete wall was completed in 1988. There have been many shipwrecks on the Gore Sands, which lie just offshore and can be exposed at low tides. The Bridgwater Corporation sent the first lifeboat to Burnham in 1836; the present rescue service is provided by the Burnham-on-Sea Area Rescue Boat. The need to protect shipping using the channel has also led to the development of the lighthouses, which are prominent landmarks. The original lighthouse, known as the Round Tower, was built to replace the light on the top of the 14th-century tower of St Andrews Church. The four-storey round tower was taken over and improved by Trinity House in 1815, and was operational until 1832. The top two storeys were later removed, to prevent confusion with the new lighthouse. The 110 feet (34 m) pillar or High Lighthouse and the low wooden pile lighthouse or Lighthouse on legs on the beach were built to replace it.
A stone pier was built in 1858 by the Somerset Central Railway. Soon afterwards, in 1860, a steamer service to Wales was inaugurated, but it was never a commercial success, and ended in 1888. Burnham-on-Sea railway station was the terminus of the Burnham branch of the Somerset and Dorset Joint Railway. It opened in 1858, closed to scheduled passenger traffic in 1951, and stopped being used for excursions in 1962. The former Great Western Railway station is now known as Highbridge and Burnham. A second pier, built of concrete between 1911 and 1914, is claimed to be the shortest pier in Britain. The town has number of educational, religious and cultural buildings, and sporting clubs. (Full article...)
Did you know...
From Wikipedia's "Did You Know" archives:
- ... that the 13th-century Hanging Chapel (pictured) in Langport has been a town hall, grammar school, museum and armoury before becoming a masonic hall?
- ... that Bridgwater Bay is the location of the last mudhorse fisherman in England?
- ... that when Farleigh Hungerford Castle was fortified from an existing manor house between 1370 and 1380, it was done without the appropriate "licence to crenellate" from the king?
- ... that Meare Pool was an important source of fish for Glastonbury Abbey before being drained between 1500 and 1750?
- ... that the busiest route of the Weston-super-Mare Tramways ran from an Old Pier to a Sanatorium?
Things you can do
 |
Here are some tasks awaiting attention:
|
WikiProjects
Nearby projects: WikiProject Bristol, WikiProject Devon, WikiProject Dorset, WikiProject Wiltshire
Topics
Recognised content
| This is a list of recognized content, updated weekly by JL-Bot (talk · contribs) (typically on Saturdays). There is no need to edit the list yourself. If an article is missing from the list, make sure it is tagged (e.g. {{WikiProject Somerset}}) or categorized correctly and wait for the next update. See WP:RECOG for configuration options. |
Featured articles
 Ælfheah of Canterbury
Ælfheah of Canterbury Bath, Somerset
Bath, Somerset Battle of Babylon Hill
Battle of Babylon Hill Battle of Marshall's Elm
Battle of Marshall's Elm Margaret Bondfield
Margaret Bondfield Robert Burnell
Robert Burnell Chew Stoke
Chew Stoke Equestrian statue of Edward Horner
Equestrian statue of Edward Horner Exmoor
Exmoor Ham Wall
Ham Wall Herbie Hewett
Herbie Hewett Kennet and Avon Canal
Kennet and Avon Canal Mells War Memorial
Mells War Memorial Mendip Hills
Mendip Hills Lionel Palairet
Lionel Palairet Porlock Stone Circle
Porlock Stone Circle River Parrett
River Parrett Sieges of Taunton
Sieges of Taunton Somerset County Cricket Club in 1891
Somerset County Cricket Club in 1891 Somerset County Cricket Club in 2009
Somerset County Cricket Club in 2009 Somerset Levels
Somerset Levels Sweet Track
Sweet Track Marcus Trescothick
Marcus Trescothick Wells Cathedral
Wells Cathedral Withypool Stone Circle
Withypool Stone Circle
Featured lists
 List of ecclesiastical parishes in the Diocese of Bath and Wells
List of ecclesiastical parishes in the Diocese of Bath and Wells Works of Keith Floyd
Works of Keith Floyd Grade I listed buildings in Bath and North East Somerset
Grade I listed buildings in Bath and North East Somerset Grade I listed buildings in Mendip
Grade I listed buildings in Mendip Grade I listed buildings in North Somerset
Grade I listed buildings in North Somerset Grade I listed buildings in Sedgemoor
Grade I listed buildings in Sedgemoor Grade I listed buildings in South Somerset
Grade I listed buildings in South Somerset Grade I listed buildings in Taunton Deane
Grade I listed buildings in Taunton Deane Grade I listed buildings in West Somerset
Grade I listed buildings in West Somerset Grade II* listed buildings in North Somerset
Grade II* listed buildings in North Somerset List of civil parishes in Somerset
List of civil parishes in Somerset List of English Heritage properties in Somerset
List of English Heritage properties in Somerset List of locks on the Kennet and Avon Canal
List of locks on the Kennet and Avon Canal List of Sites of Special Scientific Interest in Avon
List of Sites of Special Scientific Interest in Avon List of Sites of Special Scientific Interest in Somerset
List of Sites of Special Scientific Interest in Somerset List of Somerset County Cricket Club Twenty20 players
List of Somerset County Cricket Club Twenty20 players List of Somerset County Cricket Club grounds
List of Somerset County Cricket Club grounds List of Somerset County Cricket Club players with 100 or more first-class or List A appearances
List of Somerset County Cricket Club players with 100 or more first-class or List A appearances List of churches preserved by the Churches Conservation Trust in Southwest England
List of churches preserved by the Churches Conservation Trust in Southwest England List of hillforts and ancient settlements in Somerset
List of hillforts and ancient settlements in Somerset List of local nature reserves in Somerset
List of local nature reserves in Somerset List of scheduled monuments in Bath and North East Somerset
List of scheduled monuments in Bath and North East Somerset List of scheduled monuments in Mendip
List of scheduled monuments in Mendip List of scheduled monuments in North Somerset
List of scheduled monuments in North Somerset List of scheduled monuments in Sedgemoor
List of scheduled monuments in Sedgemoor List of scheduled monuments in South Somerset
List of scheduled monuments in South Somerset List of scheduled monuments in Taunton Deane
List of scheduled monuments in Taunton Deane Grade II* listed buildings in Mendip
Grade II* listed buildings in Mendip List of museums in Somerset
List of museums in Somerset List of national nature reserves in Somerset
List of national nature reserves in Somerset List of National Trust properties in Somerset
List of National Trust properties in Somerset List of scheduled monuments in West Somerset (A–G)
List of scheduled monuments in West Somerset (A–G) List of scheduled monuments in West Somerset (H–Z)
List of scheduled monuments in West Somerset (H–Z) Grade II* listed buildings in Sedgemoor
Grade II* listed buildings in Sedgemoor Grade II* listed buildings in Taunton Deane
Grade II* listed buildings in Taunton Deane Grade II* listed buildings in West Somerset
Grade II* listed buildings in West Somerset
Featured topics
Good articles
 A303 road
A303 road 1754 Taunton by-election
1754 Taunton by-election 1887 Taunton by-election
1887 Taunton by-election The Abbot's Fish House, Meare
The Abbot's Fish House, Meare Agapemonites
Agapemonites William Arnold (settler)
William Arnold (settler) Ashton Court
Ashton Court Ashton Court Festival
Ashton Court Festival Athelm
Athelm River Avon, Bristol
River Avon, Bristol Avon Gorge
Avon Gorge Herbert E. Balch
Herbert E. Balch Barrington Court
Barrington Court E. W. Bastard
E. W. Bastard Bath Abbey
Bath Abbey Bath Assembly Rooms
Bath Assembly Rooms Beckford's Tower
Beckford's Tower Berhtwald
Berhtwald Birnbeck Pier
Birnbeck Pier Bishop's Palace, Wells
Bishop's Palace, Wells Blackdown Hills National Landscape
Blackdown Hills National Landscape Blagdon Lake
Blagdon Lake John Braham (RAF officer)
John Braham (RAF officer) Brean Down
Brean Down HMS Bridgewater (L01)
HMS Bridgewater (L01) Bridgwater and Taunton Canal
Bridgwater and Taunton Canal Bridgwater Bay
Bridgwater Bay Bridgwater
Bridgwater Brislington House
Brislington House Bruton Dovecote
Bruton Dovecote Buildings and architecture of Bath
Buildings and architecture of Bath Burnham-on-Sea
Burnham-on-Sea Mike Burns (cricketer)
Mike Burns (cricketer) Buro Happold
Buro Happold Burrow Mump
Burrow Mump Burton Pynsent House
Burton Pynsent House Jenson Button
Jenson Button Allegra Byron
Allegra Byron Cadbury Camp
Cadbury Camp Cadbury Castle, Somerset
Cadbury Castle, Somerset Chard, Somerset
Chard, Somerset Cheddar Gorge
Cheddar Gorge Cheddar, Somerset
Cheddar, Somerset Chew Magna
Chew Magna St Andrew's Church, Chew Stoke
St Andrew's Church, Chew Stoke Claverton Pumping Station
Claverton Pumping Station Cleeve Abbey
Cleeve Abbey Clevedon
Clevedon Clevedon Court
Clevedon Court Clevedon Pier
Clevedon Pier Cleveland Pools
Cleveland Pools Clifton Suspension Bridge
Clifton Suspension Bridge Climate of south-west England
Climate of south-west England Coleridge Cottage
Coleridge Cottage The Crescent, Taunton
The Crescent, Taunton Crewkerne
Crewkerne Cricket at the 1900 Summer Olympics
Cricket at the 1900 Summer Olympics Crook Peak to Shute Shelve Hill
Crook Peak to Shute Shelve Hill Dolebury Warren
Dolebury Warren Dovecot at Blackford Farm
Dovecot at Blackford Farm Dunkery Hill
Dunkery Hill Dunstan
Dunstan Dunster Butter Cross
Dunster Butter Cross Dunster Castle
Dunster Castle Dunster
Dunster Dunster Working Watermill
Dunster Working Watermill Ebbor Gorge
Ebbor Gorge Exmoor pony
Exmoor pony Farleigh Hungerford Castle
Farleigh Hungerford Castle Reginald Fitz Jocelin
Reginald Fitz Jocelin Savaric FitzGeldewin
Savaric FitzGeldewin Henry Fownes Luttrell (died 1780)
Henry Fownes Luttrell (died 1780) Henry Fox (sportsman)
Henry Fox (sportsman) Frome
Frome Fyne Court
Fyne Court Gallox Bridge, Dunster
Gallox Bridge, Dunster Edith Garrud
Edith Garrud Geography of Somerset
Geography of Somerset Geology of Somerset
Geology of Somerset Gisa (bishop of Wells)
Gisa (bishop of Wells) Eleanor Glanville
Eleanor Glanville Glastonbury Abbey
Glastonbury Abbey Glastonbury Canal
Glastonbury Canal Glastonbury Festival
Glastonbury Festival Glastonbury
Glastonbury Glastonbury Lake Village
Glastonbury Lake Village Glastonbury Tor
Glastonbury Tor Grade I listed buildings in Somerset
Grade I listed buildings in Somerset Grand Western Canal
Grand Western Canal HM Prison Shepton Mallet
HM Prison Shepton Mallet Hestercombe House
Hestercombe House James Hill (British Army officer)
James Hill (British Army officer) Sidney Hill
Sidney Hill History of Somerset
History of Somerset Holnicote Estate
Holnicote Estate Hot Fuzz
Hot Fuzz Jocelin of Wells
Jocelin of Wells John of Tours
John of Tours Keynsham
Keynsham King Alfred's Tower
King Alfred's Tower King John's Hunting Lodge, Axbridge
King John's Hunting Lodge, Axbridge Scott Laird
Scott Laird Leigh Court
Leigh Court Leigh Woods National Nature Reserve
Leigh Woods National Nature Reserve Long Ashton railway station
Long Ashton railway station Lyfing (archbishop of Canterbury)
Lyfing (archbishop of Canterbury) Lytes Cary
Lytes Cary Masonic Hall, Taunton
Masonic Hall, Taunton Midsomer Norton
Midsomer Norton Minehead
Minehead Monmouth Rebellion
Monmouth Rebellion Montacute House
Montacute House Muchelney Abbey
Muchelney Abbey Nailsea Court
Nailsea Court Nailsea
Nailsea Nailsea and Backwell railway station
Nailsea and Backwell railway station Nettlecombe Court
Nettlecombe Court Stephen Newton
Stephen Newton Tom Nichols (footballer)
Tom Nichols (footballer) Nunney Castle
Nunney Castle Pill railway station
Pill railway station PinkPantheress
PinkPantheress Portishead, Somerset
Portishead, Somerset Massey Poyntz
Massey Poyntz The Priest's House, Muchelney
The Priest's House, Muchelney Prior Park Landscape Garden
Prior Park Landscape Garden Prior Park
Prior Park Pulteney Bridge
Pulteney Bridge Quantock Hills
Quantock Hills Radstock
Radstock River Brue
River Brue River Tone
River Tone Robert of Bath
Robert of Bath Roman Baths (Bath)
Roman Baths (Bath) Royal Crescent
Royal Crescent Ted Sainsbury
Ted Sainsbury St Catherine's Court
St Catherine's Court Sand Point and Middle Hope
Sand Point and Middle Hope Scheduled monuments in Somerset
Scheduled monuments in Somerset Jake Seamer
Jake Seamer Shepton Mallet
Shepton Mallet Sigeric (bishop)
Sigeric (bishop) Sir Bevil Grenville's Monument
Sir Bevil Grenville's Monument Solsbury Hill
Solsbury Hill Somerset Coal Canal
Somerset Coal Canal Somerset Coalfield
Somerset Coalfield Somerset County Cricket Club in 1882
Somerset County Cricket Club in 1882 Somerset County Cricket Club in 1885
Somerset County Cricket Club in 1885 Somerton, Somerset
Somerton, Somerset Stanton Drew stone circles
Stanton Drew stone circles Steep Holm
Steep Holm Stembridge Mill, High Ham
Stembridge Mill, High Ham Stoke sub Hamdon Priory
Stoke sub Hamdon Priory Ston Easton Park
Ston Easton Park Stoney Littleton Long Barrow
Stoney Littleton Long Barrow Street, Somerset
Street, Somerset Sutton Court
Sutton Court Sydney Gardens
Sydney Gardens St Joseph's Convent, Taunton
St Joseph's Convent, Taunton Taunton
Taunton Taunton Unitarian Chapel
Taunton Unitarian Chapel Team Bath F.C.
Team Bath F.C. Theatre Royal, Bath
Theatre Royal, Bath Tintinhull Garden
Tintinhull Garden To Catch a Copper
To Catch a Copper Treasurer's House, Martock
Treasurer's House, Martock Hugh Trenchard, 1st Viscount Trenchard
Hugh Trenchard, 1st Viscount Trenchard The Tribunal, Glastonbury
The Tribunal, Glastonbury Tyntesfield
Tyntesfield Vicars' Close, Wells
Vicars' Close, Wells Walton and Ivythorn Hills
Walton and Ivythorn Hills Watchet
Watchet Wellington Monument, Somerset
Wellington Monument, Somerset Wellington, Somerset
Wellington, Somerset Hugh of Wells
Hugh of Wells Wells, Somerset
Wells, Somerset West Hendford Cricket Ground
West Hendford Cricket Ground West Pennard Court Barn
West Pennard Court Barn West Somerset Mineral Railway
West Somerset Mineral Railway Westhay Moor
Westhay Moor Weston-super-Mare
Weston-super-Mare Westonzoyland Pumping Station Museum
Westonzoyland Pumping Station Museum Edward Wickham
Edward Wickham Maisie Williams
Maisie Williams Woodspring Priory
Woodspring Priory Wookey Hole Caves
Wookey Hole Caves Worle railway station
Worle railway station Worlebury Camp
Worlebury Camp Wulfhelm
Wulfhelm Yarn Market, Dunster
Yarn Market, Dunster Yatton railway station
Yatton railway station Yeovil
Yeovil
Good topics
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus

















































